How Can DevOps Gain Advantages from AI and ML

How DevOps Can Benefit from AI and ML
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, organizations are under constant pressure to develop, deploy, and iterate software rapidly while maintaining high quality and reliability. This demand has led to the widespread adoption of DevOps—a set of practices that combines software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) to shorten the development lifecycle and deliver continuous, high-quality software. But what is DevOps exactly, and how can it be further enhanced by integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)?
As businesses strive to keep up with the rapid pace of technological advancements, the integration of AI and ML into DevOps processes is becoming a game-changer. AI and ML offer significant potential to automate repetitive tasks, provide predictive insights, and optimize workflows, thereby taking the efficiency and reliability of DevOps practices to new heights. This blog explores the synergy between DevOps, AI, and ML, and how their integration can revolutionize software development and operations.
Understanding the Intersection of DevOps, AI, and ML
What is DevOps?
DevOps is a collaborative approach that combines software development and IT operations with the aim of shortening the development lifecycle, delivering high-quality software continuously, and improving the collaboration between development and operations teams. The goal is to enhance efficiency, reliability, and speed through automation, continuous integration, and continuous delivery.
AI and ML Basics
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence by machines, enabling them to perform tasks that typically require human intellect. Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI focused on developing algorithms that allow computers to learn from and make decisions based on data. Together, AI and ML can analyze vast amounts of data, recognize patterns, and make predictions with minimal human intervention.
Synergy between DevOps, AI, and ML
Integrating AI and ML into DevOps can significantly enhance the DevOps lifecycle by automating repetitive tasks, providing predictive insights, and optimizing processes. This integration creates a more intelligent and responsive DevOps platform, capable of delivering software more efficiently and reliably.
Benefits of AI and ML in DevOps
DevOps Automation and Efficiency
AI-driven automation can manage repetitive tasks that usually consume a lot of time and resources. For example, AI can automate code reviews, testing, and deployment processes, allowing developers to focus on more strategic tasks. This level of automation is a core aspect of DevOps automation, which accelerates the delivery pipeline and enhances productivity.
Predictive Maintenance
Using ML, teams can predict potential system failures before they occur. Predictive maintenance involves analyzing historical data to identify patterns that could indicate future issues. This proactive approach helps in reducing downtime and ensuring the reliability of the software, thereby maintaining a seamless user experience.
Enhanced Monitoring and Performance Management
AI can significantly enhance monitoring and performance management within DevOps. Machine Learning algorithms can analyze performance metrics and logs in real-time, detecting anomalies and potential issues before they impact end-users. This real-time analytics capability ensures that any performance degradation is quickly identified and addressed, maintaining optimal system performance.
Improved Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
AI and ML can optimize the CI/CD pipeline by making build and test processes smarter. For example, AI can identify which tests are most relevant for a particular build, reducing the time and resources needed for testing. In deployment, ML can suggest the best deployment strategies based on past data, minimizing risks and improving efficiency.
Security Enhancements
Security is a critical aspect of the DevOps lifecycle. AI can enhance security by identifying and responding to threats in real-time. AI-driven tools can continuously monitor systems for vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security standards. This proactive approach to security helps in safeguarding the software and the data it handles, thereby maintaining trust and compliance.
Tools and Technologies
AI and ML Tools for DevOps
Several AI and ML platforms can be integrated with DevOps tools to enhance their capabilities. Popular platforms include TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Azure ML. These platforms offer powerful AI and ML capabilities that can be leveraged to optimize DevOps processes.
DevOps Tools List with AI/ML Capabilities
Many DevOps tools now come with built-in AI and ML features. For instance, Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and CircleCI offer capabilities that can be enhanced with AI-driven automation and analytics.
Integration Strategies
To effectively integrate AI and ML into the DevOps lifecycle, it is essential to follow best practices. Start by identifying repetitive tasks that can be automated and areas where predictive analytics can add value. Use AI and ML tools that seamlessly integrate with your existing DevOps platform and ensure that your team is trained to leverage these new capabilities.
Future Trends and Predictions
Evolving AI and ML Technologies
As AI and ML technologies continue to evolve, their impact on DevOps will grow. We can expect more advanced AI-driven automation, smarter predictive analytics, and enhanced security capabilities, driving further efficiencies and innovations in DevOps.
The Future of DevOps with AI/ML
The future of DevOps lies in intelligent automation and continuous optimization. AI and ML will play a crucial role in shaping the future of DevOps practices, making them more efficient, reliable, and secure. Organizations that embrace these technologies will be better positioned to meet the demands of modern software development and operations.
Conclusion
Integrating AI and ML into DevOps offers numerous benefits, from enhanced automation and efficiency to improved security and predictive maintenance. By leveraging these technologies, organizations can transform their DevOps processes, delivering high-quality software faster and more reliably.
Protected Harbor, a leading IT Services Provider and Managed Service Provider (MSP) in the US, specializes in implementing AI and ML solutions to enhance DevOps strategies. If you’re looking to revolutionize your DevOps projects with the power of AI and ML, contact us today to learn more about our comprehensive DevOps consulting services and how we can help you achieve your goals.





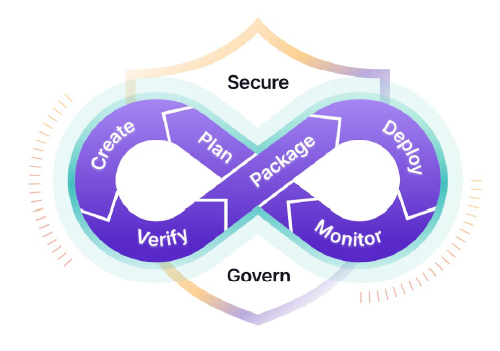 Evolution of DevOps
Evolution of DevOps

 5. Data Governance and Security: Portable queries enhance data governance and security by enforcing consistent access controls, data lineage, and auditing mechanisms across diverse data platforms. Organizations can define and enforce fine-grained access policies, ensuring that only authorized users have access to sensitive data, regardless of where it resides. Furthermore, portable queries enable organizations to maintain a centralized view of data usage, lineage, and compliance, simplifying regulatory compliance efforts.
5. Data Governance and Security: Portable queries enhance data governance and security by enforcing consistent access controls, data lineage, and auditing mechanisms across diverse data platforms. Organizations can define and enforce fine-grained access policies, ensuring that only authorized users have access to sensitive data, regardless of where it resides. Furthermore, portable queries enable organizations to maintain a centralized view of data usage, lineage, and compliance, simplifying regulatory compliance efforts.



 6. Data Security:
6. Data Security:




 Load Balancing: Load balancing distributes incoming requests for data across multiple servers or nodes to ensure optimal performance and availability. For example, a web application deployed across multiple servers may use a load balancer to distribute incoming traffic among the servers evenly. If one server becomes overloaded or unavailable, the load balancer redirects traffic to the remaining servers, ensuring that the application remains accessible and responsive. Load balancing is crucial in preventing overload situations that could lead to downtime or degraded performance.
Load Balancing: Load balancing distributes incoming requests for data across multiple servers or nodes to ensure optimal performance and availability. For example, a web application deployed across multiple servers may use a load balancer to distribute incoming traffic among the servers evenly. If one server becomes overloaded or unavailable, the load balancer redirects traffic to the remaining servers, ensuring that the application remains accessible and responsive. Load balancing is crucial in preventing overload situations that could lead to downtime or degraded performance.

 Step 5: Contact Your Internet Service Provider (ISP)
Step 5: Contact Your Internet Service Provider (ISP)

 A Real Life Scenario
A Real Life Scenario

 Future Trends and Challenges in AI TRiSM
Future Trends and Challenges in AI TRiSM