How to Prevent Crashes and Outages?
Today’s workforce relies heavily on computers for day-to-day tasks. If a computer crashes, we tend to get more than just a little agitated.
Fear of being unable to work and get our jobs done for the day races through our minds while anger takes its place in the forefront of trying to fix whatever went wrong, throwing all logic out the window.
When a system abruptly ceases to work, it crashes. The scope of a system failure can vary significantly from one that affects all subsystems to one that is just limited to a particular device or just the kernel itself.
System hang-ups are a related occurrence in which the operating system is nominally loaded. Still, the system stops responding to input from any user/device and ceases producing output. Another way to define such a system is as frozen.
This blog will explain how to prevent crashes and outages in 6 easy steps.
What is a System Crash and an Outage?
A system crash is a term used to describe a situation in which a computer system fails, usually due to an error or a bug in the software. An outage may also be caused by an application program, system software, driver, hardware malfunction, power outage, or another factor.
“A system freeze,” “system hang,” or “the blue screen of death” are the other terms for a system crash.
An outage is a general term for an unexpected interruption to a service or network. Outages can be planned (for example, during maintenance) or unplanned (a fault occurs). Outages can last for minutes, hours, days, or even weeks.
Main Reasons for Crashes and Outages
System outages can be caused by various factors, from hardware failures to software glitches. In many cases, outages are the result of a combination of factors. The following are some of the most common causes of system outages:
- Hardware failures: A defective component can cause an entire system to fail. Servers, hard drives, and other components can fail, leading to an outage.
- Software glitches: Software glitches can also cause system outages. A coding error or a bug in the software can disrupt the system’s regular operation.
- Power outages: A power outage can cause the entire system to fail. The system may be damaged permanently if the power is not restored quickly.
- Natural disasters: Natural disasters such as hurricanes, tornadoes, and earthquakes can damage or destroy critical components of the system.
System crashes can be caused by various things, from software defects to hardware failures. Sometimes, the crash may even be caused by something as simple as a power outage or due to a more severe issue, such as a virus or malware infection.
- Overheating: When a computer’s CPU or graphics card gets too hot, it can cause the system to freeze or crash. This is often the result of inadequate cooling or dust and dirt buildup inside the computer.
- Bad drivers: If a driver is outdated, corrupt, or incompatible with the operating system, it can cause the system to crash. In some cases, this can even lead to data loss or permanent damage to the computer.
 Preventions Against Crashes and Outages
Preventions Against Crashes and Outages
Nobody wants their computer to crash, but it will happen eventually. Here are a few ways to help prevent them and keep your computer running smoothly.
1. Keep Your Software Up to Date by Installing Updates
One of the best ways to prevent crashes and outages is by updating your software. This means installing updates as soon as they become available. You should also keep your operating system and programs up to date. These updates can fix bugs and security vulnerabilities, so installing them as soon as they are released is essential.
2. Avoid Clicking on Links or Downloading Files from Unknown Sources
It’s essential to be proactive in preventing crashes and outages. One way to do this is to avoid clicking on links or downloading files from unknown sources, as these can often contain malware that can harm your computer or network. Additionally, you should routinely back up your data to recover it if something goes wrong.
3. Make Sure You Have Good Antivirus and Anti-Malware Programs
One of the most important things you can do to prevent crashes is to ensure that your antivirus and anti-malware programs are up to date. These programs can help protect your computer from malware infections, which can cause crashes.
4. Close Programs You’re Not Using
One of the best ways to prevent crashes and outages is to close any programs you’re not using. When too many programs are open, your computer’s performance can suffer, leading to crashes and outages.
5. Delete Unwanted Files
Another way to improve your computer’s performance is to regularly delete files you no longer need. This will free up space on your hard drive, allowing your computer to run more efficiently.
6. Try a Trusted Disk Clean-Up to Free Up Some Space
This will help your computer run faster and smoother. You can even defragment your hard drive occasionally to keep it organized and running smoothly.
Remember to install updates for your operating system and software as soon as they are available. Keeping your computer clean and organized will help prevent crashes and outages.
Final Words
Don’t forget that you are the one running the computer, not the other way around. Therefore, it is your top priority to maintain the computers for improved performance and to continually check for any disruptions that could result in computer failures.
Try to pay attention to the little warnings your system sends you so you can save not just your computer but also yourself from a mental spiral.
Now that you know what causes crashes and outages, you can stay on top of them by following a few simple rules. Regularly monitoring your system resources, updating your software, keeping your system up to date, and having a good antivirus are the best ways to keep your computer running smoothly and keep both crashes and outages at bay.
Taking care of your data can help you to protect it from crashes and outages. You can get expert help from Protected Harbor to manage and maintain your systems and data. Protected Harbor provides an added layer of security that helps to ensure the uninterrupted flow of business-critical data. Additionally, our expert team monitors and detects any threats or updates to your system in order to ensure a smooth, efficient operation that saves it from crashing.
We help you to avoid the most common causes of data loss and system outages. These include network issues due to malicious activity, viruses, and system overload; natural disasters; power outages; and accidental deletion or corruption of data. You’re less likely to experience a system outage or lose critical data if you have a backup, plus 99.99% uptime is our guarantee.
Sign up now and get a free consultation to learn more about how Protected Harbor can keep your company’s data secure and your business up and running.







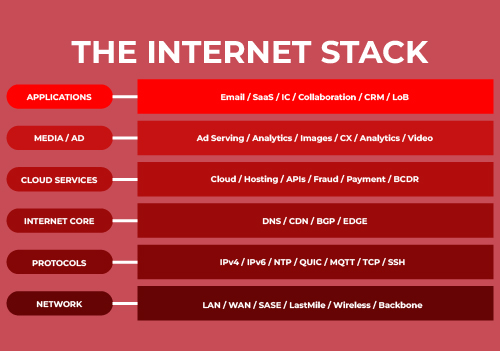


 Investigation and Expert Opinions
Investigation and Expert Opinions






 Load Balancing: Load balancing distributes incoming requests for data across multiple servers or nodes to ensure optimal performance and availability. For example, a web application deployed across multiple servers may use a load balancer to distribute incoming traffic among the servers evenly. If one server becomes overloaded or unavailable, the load balancer redirects traffic to the remaining servers, ensuring that the application remains accessible and responsive. Load balancing is crucial in preventing overload situations that could lead to downtime or degraded performance.
Load Balancing: Load balancing distributes incoming requests for data across multiple servers or nodes to ensure optimal performance and availability. For example, a web application deployed across multiple servers may use a load balancer to distribute incoming traffic among the servers evenly. If one server becomes overloaded or unavailable, the load balancer redirects traffic to the remaining servers, ensuring that the application remains accessible and responsive. Load balancing is crucial in preventing overload situations that could lead to downtime or degraded performance.

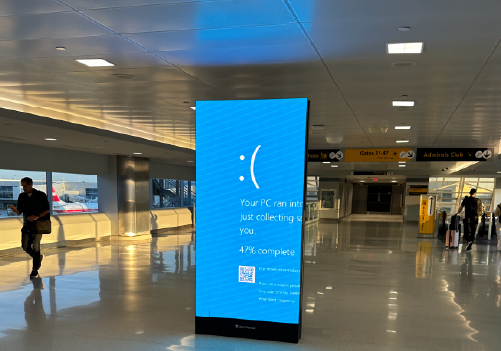
 However, during the outage, users encountered various issues such as being logged out of their Facebook accounts and experiencing problems refreshing their Instagram feeds. Additionally, Threads, an app developed by Meta, experienced a complete shutdown, displaying error messages upon launch.
However, during the outage, users encountered various issues such as being logged out of their Facebook accounts and experiencing problems refreshing their Instagram feeds. Additionally, Threads, an app developed by Meta, experienced a complete shutdown, displaying error messages upon launch.

 Preventions Against Crashes and Outages
Preventions Against Crashes and Outages
 Outages and Downtime; Is it a big deal?
Outages and Downtime; Is it a big deal?