How a Software Update Crashed Computers Globally

How a Software Update Crashed Computers Globally
And why the CrowdStrike outage is proving difficult to resolve.
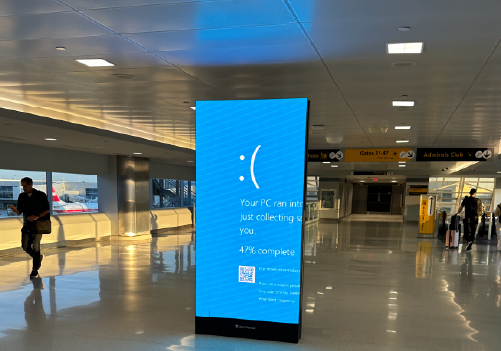
On Friday 19 July, the world experienced a rare and massive global IT outage. These events, while infrequent, can cause significant disruption. They often originate from errors in centralized systems, such as cloud services or server farms. However, this particular outage was unique and has proven to be difficult and time-consuming to resolve. The culprit? A faulty software update was pushed directly to PCs by CrowdStrike, a leading cybersecurity firm serving over half of the Fortune 500 companies.
Windows Global IT Outage: The Beginning
The outage began with a Windows global IT outage stemming from faulty code distributed by CrowdStrike. This update caused affected machines to enter an endless reboot loop, rendering them offline and virtually unusable. The severity of the problem was compounded by the inability to issue a fix remotely.
Immediate Impacts of the IT Outage
The immediate aftermath saw a widespread Microsoft server down scenario. Systems across various industries were disrupted, highlighting the dependency on stable cybersecurity measures. With computers stuck in an endless cycle of reboots, normal business operations ground to a halt, creating a ripple effect that was felt globally.
The Challenges of a Remote Fix
Why the Global IT Outage is Harder to Fix
One of the most significant challenges in this global IT outage is the inability to resolve the issue remotely. The faulty code rendered remote fixes ineffective, necessitating manual intervention. This meant that each affected machine had to be individually accessed to remove the problematic update.
Manual vs. Automated Fixes
Unless experts can devise a method to fix the machines remotely, the process will be painstakingly slow. CrowdStrike is exploring ways to automate the repair process, which would significantly expedite resolution. However, the complexity of the situation means that even an automated solution is not guaranteed to be straightforward.
Broader Implications of the Outage
Understanding the Broader Impact
The Windows global IT outage has exposed vulnerabilities in how updates are managed and deployed. This incident serves as a stark reminder of the potential risks associated with centralized update systems. Businesses worldwide are now reevaluating their dependence on single-point updates to avoid similar disruptions in the future.
Preventing Future IT Outages
Moving forward, organizations could implement more rigorous testing protocols and fail-safes to prevent such widespread disruptions. Additionally, there may be a shift towards more decentralized update mechanisms to minimize the risk of a single point of failure.
Conclusion
The global IT outage caused by a faulty CrowdStrike update serves as a critical lesson for the tech industry. The incident underscores the need for more resilient and fail-safe update mechanisms to ensure that such disruptions do not occur again. As organizations worldwide continue to grapple with the consequences, the focus will undoubtedly shift towards preventing future occurrences through improved practices and technologies.
FAQs
What caused the global IT outage?
The outage was caused by a faulty CrowdStrike software update, which led to affected computers to enter an endless reboot loop.
How widespread was the outage?
The outage was global, affecting businesses and systems across various industries worldwide.
Why is it difficult to fix the outage?
The affected machines cannot be remotely fixed due to the nature of the faulty code. Each computer needs to be manually accessed to remove the problematic update.
Is there a way to automate the fix?
CrowdStrike is exploring automated solutions, but the complexity of the issue means that a straightforward automated fix may not be feasible.
What are the broader implications of the outage?
The incident highlights the vulnerabilities in centralized update systems and may lead to more rigorous testing protocols and decentralized update mechanisms.
How can future IT outages be prevented?
Implementing more robust testing procedures and decentralized update systems can help prevent similar outages in the future.







 Additional Key Features
Additional Key Features

 Evolution of DevOps
Evolution of DevOps

 5. Data Governance and Security: Portable queries enhance data governance and security by enforcing consistent access controls, data lineage, and auditing mechanisms across diverse data platforms. Organizations can define and enforce fine-grained access policies, ensuring that only authorized users have access to sensitive data, regardless of where it resides. Furthermore, portable queries enable organizations to maintain a centralized view of data usage, lineage, and compliance, simplifying regulatory compliance efforts.
5. Data Governance and Security: Portable queries enhance data governance and security by enforcing consistent access controls, data lineage, and auditing mechanisms across diverse data platforms. Organizations can define and enforce fine-grained access policies, ensuring that only authorized users have access to sensitive data, regardless of where it resides. Furthermore, portable queries enable organizations to maintain a centralized view of data usage, lineage, and compliance, simplifying regulatory compliance efforts.




 The certification for SOC 2 comes from an independent auditing procedure that ensures IT service providers securely manage data to protect the interests of an organization and the privacy of its clients. For security-conscious businesses, SOC 2 compliance is a minimal requirement when considering a Software as a Service (SaaS) provider. Developed by the American Institute of CPAs (AICPA), SOC 2 defines criteria for managing customer data based on five “trust service principles” – security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
The certification for SOC 2 comes from an independent auditing procedure that ensures IT service providers securely manage data to protect the interests of an organization and the privacy of its clients. For security-conscious businesses, SOC 2 compliance is a minimal requirement when considering a Software as a Service (SaaS) provider. Developed by the American Institute of CPAs (AICPA), SOC 2 defines criteria for managing customer data based on five “trust service principles” – security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.

 However, during the outage, users encountered various issues such as being logged out of their Facebook accounts and experiencing problems refreshing their Instagram feeds. Additionally, Threads, an app developed by Meta, experienced a complete shutdown, displaying error messages upon launch.
However, during the outage, users encountered various issues such as being logged out of their Facebook accounts and experiencing problems refreshing their Instagram feeds. Additionally, Threads, an app developed by Meta, experienced a complete shutdown, displaying error messages upon launch.

 4. Quantum Computing’s Quantum Leap
4. Quantum Computing’s Quantum Leap

