How to defend against email impersonation attacks

12 Ways to Defend Against Email Impersonation Attacks: Your Ultimate Guide
Welcome to the third blog of Cybersecurity Awareness Month 2024, brought to you by Protected Harbor. In this article, we aim to analyze the growing threat of email impersonation attacks and provide actionable strategies to defend against these malicious attempts. Email impersonation is a rising concern globally, targeting both individuals and organizations to extract sensitive information or force financial transactions. Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge needed to protect yourself and your organization.
Understanding Email Impersonation Attacks
Before diving into defense strategies, it’s crucial to understand how these attacks work. Email impersonation often combines social engineering with technical manipulation, tricking recipients into believing they are communicating with trusted sources. Here are the most common forms of email impersonation attacks:
- CEO Scams- In CEO scams, cybercriminals impersonate high-level executives, such as the CEO or CFO, to trick employees into transferring sensitive information or funds.
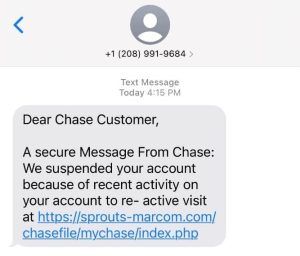
- Phishing- Phishing involves attackers pretending to be a legitimate entity like a bank or online retailer, attempting to collect sensitive information or login credentials from the victim.
- Spoofing- Email spoofing is when attackers fake the sender’s email address to make it appear as if it’s coming from a trusted source, but it’s actually sent from a fraudulent address.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC)- BEC attacks occur when attackers impersonate business partners, vendors, or suppliers to request financial transfers or sensitive information under false pretenses.
Top 12 Ways to Defend Against Email Impersonation Attacks
To protect against these attacks, a multi-layered approach is essential, involving both technical and human controls. Below are 12 effective strategies to defend against email impersonation attacks:
- Implement DMARC- Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) helps organizations define how unauthenticated emails should be handled and provides reporting mechanisms to monitor suspicious email activity.
- Use SPF and DKIM- Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) validate the sender’s domain and email content integrity. These tools verify that an email’s sender matches the domain it claims to be from, preventing spoofing.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)- Adding an extra layer of security through 2FA ensures that even if login credentials are stolen, the attacker cannot access the email without a second verification, such as a text message or app-generated code.
- Use Email Encryption- Encryption ensures that email contents are protected during transmission. Only the intended recipient can decrypt and access the message, making it difficult for attackers to intercept sensitive information.
- Develop a Clear Email Security Policy- Creating a comprehensive email security policy is essential for defining how to handle emails containing sensitive information, how to report suspicious messages, and the procedures for responding to email impersonation attempts.
- Conduct Regular Security Awareness Training- Cybersecurity training should be a continuous process. Regular training sessions will help employees identify phishing attempts, suspicious links, and spoofed emails, reducing the chances of falling victim to these attacks.
- Implement Advanced Email Filtering- Email filters can block suspicious messages before they reach employees’ inboxes. Advanced filtering tools can flag or block emails from unknown senders, or those that use suspicious keywords or attachments.
- Monitor Email Activity Regularly- Routine monitoring of email activity can help identify patterns or anomalies that may indicate an ongoing impersonation attempt. Early detection allows organizations to mitigate the threat before it escalates.
- Verify Sender Information- Always double-check the sender’s email address and domain before acting on any requests. Attackers often use subtle changes in email addresses to impersonate legitimate senders.
- Be Wary of Urgent or Threatening Emails- Be cautious of emails that attempt to create a sense of urgency, such as threats to cancel services or warnings about unauthorized account access. Attackers use these tactics to pressure victims into acting without thinking.
- Use Strong Passwords- Ensure that all email accounts are protected with strong, unique passwords. Avoid using the same password across multiple platforms, and change passwords regularly.
- Report Suspicious Emails- Always report suspicious emails to your IT department or email service provider. Quick action can prevent an impersonation attempt from becoming a successful attack.
 Best Cybersecurity Practices for Individuals
Best Cybersecurity Practices for Individuals
While organizations are prime targets, individuals are equally vulnerable. Here are some key practices to stay secure:
- Use a Secure Email Provider- Opt for email providers that offer enhanced security features like encryption and two-factor authentication.
- Use a Password Manager- A password manager helps generate and store strong, unique passwords for every account, eliminating the risk of password reuse across multiple platforms.
- Be Careful with Public Wi-Fi- Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured, making it easier for attackers to intercept communications. Avoid accessing sensitive information over public Wi-Fi.
- Keep Software Updated- Outdated software often contains vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Ensure your email clients, operating systems, and other software are regularly updated with the latest security patches.
Best Cybersecurity Practices for Organizations
Organizations must adopt a proactive approach to email security. Here are some best practices:
- Implement an Incident Response Plan- An incident response plan outlines the steps to take if an email impersonation attack is detected. Having a plan in place allows for a swift and coordinated response.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits- Frequent security audits help identify vulnerabilities in your email systems before attackers can exploit them.
- Use Email Authentication Protocols Implementing DMARC, SPF, and DKIM helps ensure that only legitimate emails reach your employees, reducing the risk of impersonation.
- Provide Regular Security Awareness Training- Ongoing training ensures that employees stay informed about the latest tactics used in email impersonation attacks and know how to report suspicious activity.
Conclusion
Email impersonation attacks pose a significant threat to individuals and organizations alike. By implementing the strategies discussed in this article, you can drastically reduce your risk of falling victim to these sophisticated attacks. Protected Harbor is committed to safeguarding organizations with comprehensive cybersecurity solutions tailored to modern threats, including email impersonation attacks.
At Protected Harbor, we go beyond standard security measures by employing advanced cybersecurity tools and techniques designed to counter evolving threats. Our solutions include cutting-edge email filtering systems powered by AI-based threat detection, real-time monitoring, and automated incident response. Additionally, our anomaly detection systems identify unusual email behaviors that could signal an impersonation attack, while zero-trust frameworks ensure that each action within your network is continuously verified.
Moreover, our services are Secure by Design, meaning we integrate security protocols at every layer of your organization’s infrastructure from the ground up. From robust encryption to multi-factor authentication, we build systems with security as a core feature, not an afterthought. With our expertise, Protected Harbor provides a shield of protection against evolving cyber risks, ensuring your organization’s digital assets and sensitive information remain secure.
Take proactive steps today and trust Protected Harbor to safeguard your email systems with our best-in-class cybersecurity technologies. Reach out for a consultation and free IT Audit and fortify your defenses against email impersonation attacks.
FAQs: How to Defend Against Email Impersonation Attacks
1. What is an email impersonation attack?
An email impersonation attack occurs when an attacker sends an email that appears to come from a legitimate source to deceive the recipient into sharing sensitive information or performing a certain action.
2. How do email impersonation attacks work?
Attackers usually spoof an email address, making the email appear as if it’s from a trusted sender. They may include malicious links, attachments, or requests for sensitive data.
3. How can I identify an email impersonation attack?
Look for unusual requests, grammatical errors, and discrepancies in the email address or domain. Be wary of messages demanding urgent action or sensitive information.
4. What should I do if I receive an email impersonation attack?
Do not reply or click on any links. Report the email to your IT team or email provider and delete it.
5. How can I prevent email impersonation attacks?
Implement security protocols like DMARC, SPF, and DKIM, use strong passwords, and enable two-factor authentication for added protection.
6. How can I educate my employees about email impersonation attacks?
Regularly train your employees on recognizing, reporting, and responding to email threats. Ensure they understand the importance of following email security policies.











 Top Phishing Email Attacks to Watch For
Top Phishing Email Attacks to Watch For




 Impact Of Angler Phishing Attacks on Business
Impact Of Angler Phishing Attacks on Business