Security Measures Every Law Firm Should Implement

Security Measures Every Law Firm Should Implement
Few entities handle information as confidential and discreet as law firms. Legal practices deal with clients, cases, and documents containing private and often privileged data. Safeguarding this information has become integral to a law firm’s responsibility.
In this blog post, we discuss the critical topic of data security for law firms, specifically focusing on one of the most fundamental and adequate security measures – email encryption. In addition, we will go beyond email encryption to examine a broader range of security measures law firms should consider to fortify their defenses against potential threats.
Email Encryption in Law Firms
Email encryption is a security measure that transforms the content of an email into a coded format, making it accessible only to authorized recipients. Email encryption is critical for law firms due to the highly confidential nature of legal information. Clients entrust law firms with sensitive data, from personal details to privileged legal documents. Failing to protect this information can result in legal and ethical repercussions and damage the reputation and trust of the law firm. Email encryption is the frontline defense in safeguarding this data.
Sensitive legal information frequently communicated via email includes confidential client communications, contracts, legal opinions, intellectual property documents, case files, and financial data. These documents often contain susceptible details that, if exposed, can have severe consequences for clients and the law firm.
Risks Associated with Unencrypted Email Communication
You may or may not know that during transmission, emails can be intercepted, either in transit or on the recipient’s end, by malicious actors. Unauthorized access to such information can lead to data breaches and legal breaches of confidentiality. Numerous email-related security breaches in the legal sector have underlined the real-world risks associated with unencrypted email communication.
Benefits of Email Encryption
1. Email encryption protects client confidentiality
Email encryption ensures that only authorized individuals can access the contents of an email. This helps maintain the client data security, strict attorney-client privilege is vital in the legal profession. Clients can be assured that their sensitive information remains confidential and protected.
2. Compliance with data privacy regulations
Email encryption aids law firms in complying with data privacy regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). These regulations require strict protection of personal and health data, respectively. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties.
3. Encryption can prevent data breaches
Encryption adds an extra layer of security to emails, making it exceptionally challenging for cybercriminals to exploit vulnerabilities. Data breaches can have catastrophic consequences, including damage to reputation and potential legal liability. Email encryption significantly reduces the risk of such breaches.
How to Implement Email Encryption
Here’s a quick step-by-step guide for law firms to set up email encryption:
- Evaluate your law firm’s email needs and requirements.
- Choose a reliable email encryption solution or service. (please list three different services)
- Generate encryption keys and manage them securely.
- Implement the chosen encryption solution across all email communication.
- Train your staff on using the encryption tools effectively.
- Regularly update and monitor your email encryption system.
Best Practices for Email Encryption
- Regularly update encryption software to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Train your employees on recognizing phishing attempts and maintaining secure email practices.
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to ensure the effectiveness of your email encryption setup.
 Additional Security Measures for Law Firms
Additional Security Measures for Law Firms
- Importance of strong password policies: Strong password policies are essential for safeguarding sensitive data. Law firms should enforce policies that require complex passwords, regular password changes, and prohibit password sharing. Passwords are often the first defense against unauthorized access and should not be taken lightly.
- The need for two-factor authentication (2FA) in law firms: Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a crucial security layer. It requires users to provide two forms of identification before accessing accounts: something they know (password) and something they have (e.g., a mobile device). 2FA significantly enhances security, preventing unauthorized access even if a password is compromised.
- Secure file-sharing and document management systems: Implementing secure file-sharing and document-management systems is imperative. These systems offer controlled access to sensitive legal documents, ensuring only authorized personnel can view, edit, or share them. It also keeps a log of activities, which is essential for accountability.
Training and Employee Awareness
- Role of employee training in maintaining security: Regular training on safety best practices is vital. It educates staff on identifying potential threats and maintaining a secure digital environment and preventing data breaches in law firms. Training should be ongoing to keep employees informed about evolving security risks.
- Importance of educating staff on phishing threats: Phishing attacks are common in the legal sector. Educating staff on recognizing phishing attempts, suspicious email links, or attachments is crucial in preventing data breaches.
- The need for a security-conscious workplace culture: Creating a culture of security awareness is paramount. Employees should understand the significance of security measures and view them as integral to their roles. Regular reminders and incentives can reinforce the importance of maintaining a security-conscious workplace culture.
What is a Law Firm’s Data Security Risk?
Failing to maintain robust IT security poses significant risks for your firm and can have severe consequences for your clients. Law firms are particularly attractive to hackers and cybercriminals due to the valuable information they hold, such as trade secrets, intellectual property, merger and acquisition details, personally identifiable information (PII), and confidential attorney-client data.
Despite these cybersecurity risks, law firms are obligated to protect their clients’ information and ensure client confidentiality. A breach in security can lead to extensive consequences, from minor embarrassments to serious legal issues, including:
- Compromised communications due to phished or hacked email accounts
- Inaccessibility to firm information due to ransomware attacks, where hackers encrypt files and demand payment to restore access
- Public leaks of personal or business information, potentially on social media
- Loss of public and client trust in your firm
- Malpractice allegations and lawsuits
Implementing robust cybersecurity measures for law firms is crucial to protecting sensitive information and maintaining client confidentiality.
What are your ethical and regulatory obligations?
As a law firm, your ethical and regulatory obligations regarding client data security are paramount. The legal profession is bound by strict standards that require the safeguarding of sensitive client information, making cybersecurity for law firms a critical concern. Law firms must ensure that they comply with relevant data protection laws and ethical guidelines to protect client confidentiality and avoid severe legal and financial consequences.
Regulatory bodies impose stringent requirements on how law firms handle and protect client data. For example, the American Bar Association (ABA) mandates that attorneys take reasonable steps to protect client information from unauthorized access or disclosure. This includes implementing robust cybersecurity measures to prevent data breaches in law firms, such as encryption, secure access controls, and regular security audits.
Furthermore, data protection laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) may apply to law firms, depending on their location and the nature of their client base. These regulations require law firms to adopt comprehensive data protection strategies to ensure the security and privacy of client information.
By fulfilling these ethical and regulatory obligations, law firms can mitigate risks, maintain client trust, and uphold their professional responsibilities. Preventing data breaches in law firms is not only a legal requirement but also a crucial aspect of maintaining the integrity and reputation of the legal profession.
Data Backups and Disaster Recovery
Regular data backups are essential in case of data loss due to hardware failure, human error, or cyberattacks. It ensures that critical data can be restored, minimizing downtime and potential data loss.
Creating a disaster recovery plan is a proactive step that outlines the actions to be taken during a data breach or a disaster. This plan should cover data recovery, communication strategies, and roles and responsibilities.
Cloud-based backup solutions offer scalable and secure data storage. They enable law firms to securely store data off-site, ensuring data availability even if on-site systems fail.
Compliance with Legal and Industry Standards
Law firms must adhere to various regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and specific legal industry standards. Failure to comply with these standards can result in legal consequences, including fines and sanctions.
Encryption and other security measures are essential components of compliance. They help protect sensitive data and ensure that the firm adheres to data protection and privacy regulations.
Non-compliance with legal and industry standards can lead to legal liability, fines, damage to reputation, and loss of client trust. Law firms must understand and adhere to these standards.
Conclusion
The legal profession’s reputation for discretion and trust is at the heart of its practice, and the consequences of data breaches or leaks can be devastating. Email encryption and the security measures we’ve discussed are not mere recommendations; they are imperative for law firms to fulfill their ethical and legal obligations while upholding their clients’ trust.
We strongly encourage law firms to take immediate action to enhance their data security. Proactive measures can prevent potential disasters and reinforce your reputation as a reliable and secure legal partner.
If you’re part of a law firm or legal practice, now is the time to assess your security practices. Ensure your digital defenses are strong and your client’s data is protected.
Protected Harbor is a leading IT and security services provider for law firms in the US. Our team specializes in securing legal data, ensuring compliance, and maintaining a robust defense against evolving threats.
Your data’s security is our top priority, and we are here to help you navigate the ever-changing landscape of digital threats and compliance regulations. Together, we can protect your clients, reputation, and future.





 Myth #3: Two-Factor Authentication is Infallible – No Need for Additional Security Measures
Myth #3: Two-Factor Authentication is Infallible – No Need for Additional Security Measures
 Threat Detection and Response Best Practices
Threat Detection and Response Best Practices

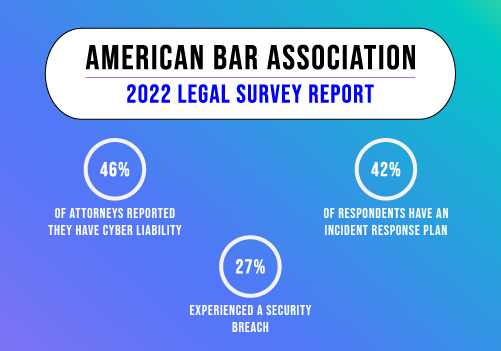



 6. Regularly Update Software and Systems
6. Regularly Update Software and Systems












 1. Bridgestone
1. Bridgestone